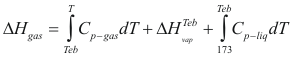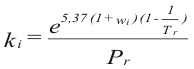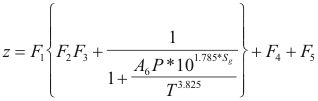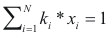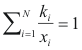INTERESTING CALCULATIONS
TOWER
-
Calculate of the haulage of liquids for the vapor
- Calculate of the flooding of the trays
PIPES
-
Calculate of the decibels taken place by the step of the fluid in the pipe
PUMPS
- Calculate of the minimum pressure before the cavitation
VALVES
- Calculate of the minimum pressure before the cavitation
FURNACES
- Calculate the consumption of the fuel
- Calculate of the reactions happened among of the tubes
BOILERS
- Calculate of the sure diameter of the pipe of the boiler
- Calculate of the lost of heat of the boiler
- Calculate of the reactions happened by the contamination
HEAT EXCHANGERS
- Calculate of the temperature of the tube
- Calculate of the flow with phase change.
Density - program online for pure compound
For liquids
to obtain the density of a liquid the following formula is used:
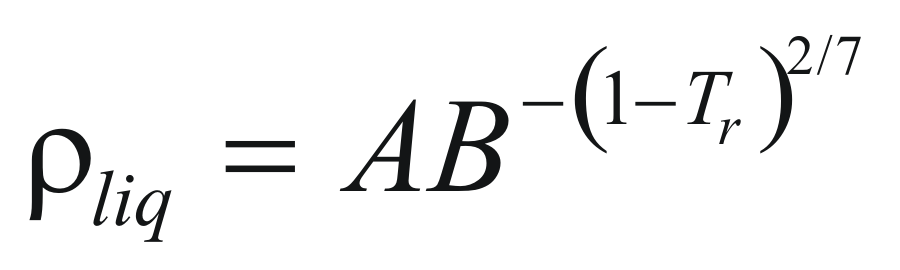
Where ρliq is the density of the pure liquid (gr/cm3)
A and B are constant that they depend on the compound.
Tr is the reduced temperature.
For the Gases
to obtain the density of a gas the following formula is used:
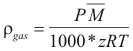
Where ρgas is the density of the gas (gr/cm3)
P is the total pressure (Atm)
M is the molecular weight (gr).
z is the factor of compressibility of the gas.
T is the temperature of the gas (°K)
R is the constant of the gas = 0.082
For the Mixture
to obtain the density average of the mixture the following formula is used
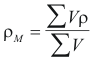
Where ρM is the density average of the mixture (gr/cm3)
ρ is the density of the component i (gr/cm3)
V is the volume that occupies according to its fraction molar (cm3)
Special case in density of hydrocarbons
Viscosity - program online for pure compound
; For the liquids
to obtain the viscosity of a liquid the following formula is used:
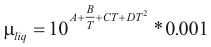
Where μliq is the viscosity of the liquid (kg/m*s)
A, B, C and D are constant that it depends on the compound
T is the temperature (°K)
For the gases
to obtain the viscosity of a gas the following formula is used:
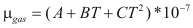
Where μgas is the viscosity of the gas (kg/m*s)
A, B and C are constant that it depends on the compound
T is the temperature (°K)
For the Mixture
to obtain the viscosity of the mixture the following formula is used
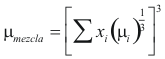
Where μmixture is the viscosity of the mixture (kg/m*s)
μi is the viscosity of each compound (kg/m*s)
xi is the fraction molar of the mixture
Caloric capacity
For the liquids
to obtain the caloric capacity of a liquid the following formula is used:
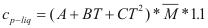
Where Cp-liq is the caloric capacity of a pure liquid (cal/mol-°K).
A, B and C are constant that they depend on the compound
T is the temperature to which is the liquid. (°K)
M is the molecular weight of the compound (gr).
For the gases
to obtain the caloric capacity of a gas the following formula is used:
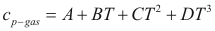
Where Cp-gas is the caloric capacity of a gas (cal/mol-°K).
A, B, C and D are constant that they depend on the compound
T is the temperature. (°K)
For the mixture
to obtain the caloric capacity the mixture the following formula is used:
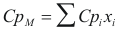 o
o
Where CpM is the caloric capacity of the mixture (cal/mol°K)
Cpi is the caloric capacity of the component i (cal/mol°K).
xi is the fraction molar of the component i
Thermal Conductivity
For the liquids
to obtain the thermal conductivity of a liquid the following formula is used:
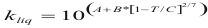
Where kliq is the thermal conductivity of the pure liquid (w/m°K)
A, B, C is constant that they depend on the liquid
T is the temperature (°K)
For the gases
to obtain the thermal conductivity of a gas the following formula is used:
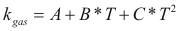
Where kgas is the thermal conductivity of the gas (w/m°K)
A, B, C is constant that it depends on the gas.
T is the temperature (°K)
For the mixture
to obtain the thermal conductivity of the mixture the following formula is used:
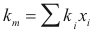
Where km is the thermal conductivity of the mixture (w/m°K)
ki is the thermal conductivity of the component i
xi is the fraction molar of the component i.
Latent heat of Vaporization
For a pure compound
to obtain the latent heat of vaporization the following formula is used:
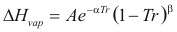
Where ΔHvap is the latent heat of vaporization (kj/mol)
A, α, β is constant that it depends on the compound
Tr is the reduced temperature
Enthalpy
For the liquids
to obtain the genitalia of a liquid the following formula is used:
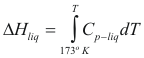 ole13.gif
ole13.gif
Where ΔHliq is the enthalpy of the liquid (cal/mol)
Cp-liq is the caloric capacity of the liquid (cal/mol°K)
T is the temperature of the liquid (°K)
For the gases
to obtain the enthalpy of a gas the following formula is used:
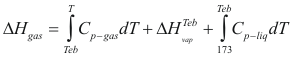
Where ΔHgas is the enthalpy of the gas (cal/mol)
Cp-gas is the caloric capacity of the gas (cal/mol°K)
ΔHvap is the latent heat of vaporization (kj/mol)
Cp-liq is the caloric capacity of the liquid (cal/mol°K)
T is the temperature of the liquid (°K)
Teb is the temperature of boil to a given pressure.
Factor ki - program online for pure compound
to obtain the factor ki of each compound is used their properties you criticize and value asentric:
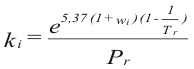
Where Pr is the reduced pressure
Tr is the reduced temperature
ω is the factor asentric
Factor Z - program online for pure compound
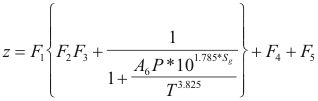
Where z is the factor of compressibility.
T is the temperature(°R)
P is the pressure (psi) (P <5000 psi)
Sg is the specifies gravity. (0.5 - 0.8)
F1 = P(0.251*Sg-0.15)-0.202*Sg+1.106
F2=1.4e-0.0054(T-460).
F3=A1*P5+A2*P4+A3*P3+A4*P2+A5*P
F4={0.154-0.152*Sg}*P(3.185*Sg-1)e-0.5*P-0.02
F5=0.35*{(0.6-Sg)E-1.039(P-1.8)2}
A1=0.001946
A2=-0.027635
A3=0.136315
A4=-0.23849
A5=0.105168
A6=3.44x108
Temperature of boil - program online for pure compound
to calculate the temperature of boil of a mixture the following equality should be completed:
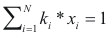
Where ki is the balance coefficient to a pressure and given temperature.
xi is the fraction molar of the compound i.
.
Condensation temperature - program online for pure compound
to calculate the temperature of condensation of a mixture the following equality should be completed:
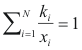
Where ki is the balance coefficient to a pressure and given temperature.
xi is the fraction molar of the compound i.
Chart for the conductivity thermal of the gas
| Formula |
Compound |
A |
B |
C |
TMIN |
TMAX |
| N2 |
Nitrogen |
0.00283 |
8.125E-05 |
-0.00000002 |
| CO2 |
Dioxide Carbon |
-0.012 |
0.00010208 |
-0.000000022403 |
195 |
1500 |
| H2S |
Sulfur hydrogen |
| H2O |
Water |
0.00193 |
4.52E-05 |
0.00000005 |
| C1 |
Methane |
-0.00935 |
0.00014028 |
0.00000003318 |
97 |
1400 |
| C2 |
Ethane |
-0.01936 |
0.00012547 |
0.00000003829 |
225 |
825 |
| C3 |
Propane |
-0.00869 |
6.6409E-05 |
0.00000007876 |
233 |
773 |
| i-C4 |
i-Butane |
-0.00115 |
1.4943E-05 |
0.00000014921 |
261 |
673 |
| n-C4 |
n-Butane |
-0.00182 |
1.9396E-05 |
0.00000013818 |
225 |
675 |
| i-C5 |
i-Pentane |
-0.00389 |
3.1816E-05 |
1.0396E-07 |
250 |
475 |
| n-C5 |
n-Pentane |
0.00137 |
1.8081E-05 |
1.2136E-07 |
225 |
480 |
| C6 |
n-Hexane |
-0.002 |
7.779E-06 |
1.3824E-07 |
290 |
480 |
| C7 |
n-Heptane |
-0.00172 |
1.6565E-05 |
1.0525E-07 |
250 |
750 |
| C8 |
n-Octane |
-0.00213 |
1.8456E-05 |
9.4775E-08 |
300 |
800 |
| C9 |
n-Nonane |
-0.00655 |
3.2637E-05 |
7.715E-08 |
449 |
678 |
| C10 |
n-Decane |
-0.00113 |
8.109E-06 |
9.6092E-08 |
470 |
700 |
| C11 |
n-Undecane |
0.01364 |
-4.8303E-05 |
1.4396E-07 |
470 |
800 |
| C12 |
n-Dozedecane |
-0.00812 |
2.915E-05 |
7.2085E-08 |
489 |
1000 |
| C2H4O2 |
Acid acetic |
0.00234 |
-6.5956E-06 |
1.1569E-07 |
295 |
687 |
| C2H2 |
Acetylene |
-0.00358 |
6.2542E-05 |
7.0646E-08 |
200 |
600 |
| C3H6O |
Acetone |
-0.00084 |
8.7475E-06 |
1.0678E-07 |
273 |
572 |
| NH3 |
Ammoniac |
| CO |
Monoxide Carbon |
0.00158 |
8.2511E-05 |
-1.9081E-08 |
70 |
1250 |
| CH2CH2 |
Ethylene |
-0.00123 |
3.6219E-05 |
1.2459E-07 |
150 |
750 |
| O2 |
Oxygen |
0.00181 |
8.575E-05 |
-2E-08 |
| C4H8 |
i-Butylene |
-0.00327 |
3.0146E-05 |
1.2529E-07 |
250 |
850 |
| C3H6 |
Propylene |
-0.01116 |
7.5155E-05 |
6.5558E-08 |
250 |
1000 |
| CH3OH |
Methanol |
0.00234 |
5.434E-06 |
1.3154E-07 |
273 |
684 |
| C2H5OH |
Ethanol |
-0.00556 |
4.362E-05 |
8.5033E-08 |
351 |
991 |
| C6H6 |
Benzene |
-0.00565 |
3.4493E-05 |
6.9298E-08 |
325 |
700 |
| neo-C5 |
neo-Pentane |
0.00071 |
-8.1028E-06 |
1.8759E-07 |
270 |
425 |
Chart for the conductivity thermal of the liquid
| Formula |
Compound |
A |
B |
C |
TMIN |
TMAX |
| N2 |
Nitrogen |
| CO2 |
Dioxide Carbon |
-1.3679 |
0.8092 |
304.19 |
217 |
289 |
| H2S |
Sulfur hydrogen |
| H2O |
Water |
-0.27070528 |
0.00456253 |
-0.00000546 |
| C1 |
Methane |
-1.0976 |
0.5387 |
190.58 |
91 |
181 |
| C2 |
Ethane |
-1.3474 |
0.7003 |
305.42 |
90 |
290 |
| C3 |
Propane |
-1.2127 |
0.6611 |
369.82 |
85 |
351 |
| i-C4 |
i-Butane |
-1.6862 |
0.9802 |
408.14 |
114 |
388 |
| n-C4 |
n-Butane |
-1.8929 |
1.2885 |
425.18 |
135 |
404 |
| i-C5 |
i-Pentane |
-1.6824 |
0.9955 |
460.43 |
113 |
437 |
| n-C5 |
n-Pentane |
-1.2287 |
0.5322 |
469.65 |
143 |
446 |
| C6 |
n-Hexane |
-1.8389 |
1.186 |
507.43 |
178 |
482 |
| C7 |
n-Heptane |
-1.8482 |
1.1843 |
540.26 |
183 |
513 |
| C8 |
n-Octane |
-1.8388 |
1.1699 |
568.83 |
216 |
540 |
| C9 |
n-Nonane |
-1.7865 |
1.1033 |
595.65 |
220 |
566 |
| C10 |
n-Decane |
-1.7768 |
1.0839 |
618.45 |
243 |
588 |
| C11 |
n-Undecane |
-1.6318 |
0.9325 |
638.76 |
248 |
607 |
| C12 |
n-Dozedecane |
-1.7989 |
1.1109 |
658.2 |
264 |
625 |
| C2H4O2 |
Acid acetic |
-1.2836 |
0.5893 |
592.71 |
290 |
563 |
| C2H2 |
Acetylene |
| C3H6O |
Acetone |
-1.3857 |
0.7643 |
508.2 |
178 |
483 |
| NH3 |
Ammoniac |
| CO |
Monoxide Carbon |
-1.7115 |
1.1359 |
132.92 |
68 |
126 |
| CH2CH2 |
Ethylene |
-1.3314 |
0.8527 |
282.26 |
104 |
268 |
| O2 |
Oxygen |
| C4H8 |
i-Butylene |
-1.49020 |
0.8491 |
417.90 |
133 |
397 |
| C3H6 |
Propylene |
-1.43760 |
0.7718 |
364.76 |
88 |
347 |
| CH3OH |
Methanol |
-1.1793 |
0.6191 |
512.58 |
175 |
487 |
| C2H5OH |
Ethanol |
-1.3172 |
0.6987 |
516.25 |
159 |
490 |
| C6H6 |
Benzene |
-1.6846 |
1.052 |
562.16 |
279 |
534 |
| neo-C5 |
neo-Pentane |
-1.7534 |
1.0306 |
433.78 |
257 |
412 |
BACK
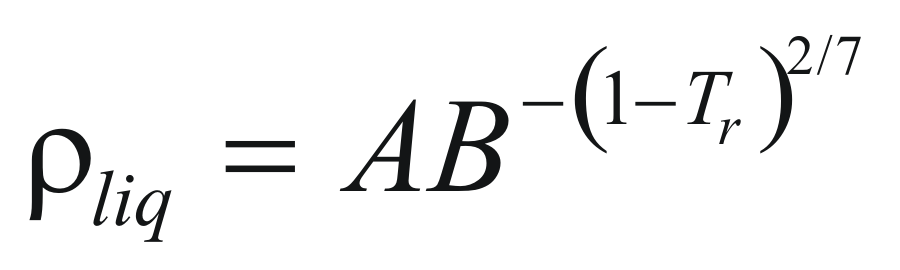
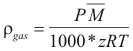
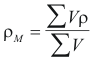
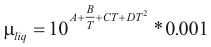
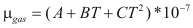
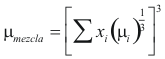
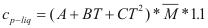
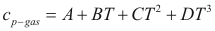
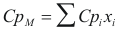 o
o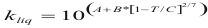
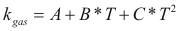
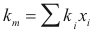
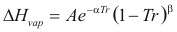
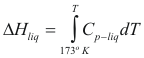 ole13.gif
ole13.gif